4.1Pandas介绍
学习目标
- 目标
- 了解Numpy与Pandas的不同
- 了解Pandas的MultiIndex与panel结构
- 说明Pandas的Series与Dataframe两种结构的区别
- 应用
- 股票涨跌幅数据的修改
4.1.1 Pandas介绍
- 2008年WesMcKinney开发出的库
- 专门用于数据挖掘的开源python库
- 以Numpy为基础,借力Numpy模块在计算方面性能高的优势
- 基于matplotlib,能够简便的画图
- 独特的数据结构
4.1.2 为什么使用Pandas
Numpy已经能够帮助我们处理数据,能够结合matplotlib解决部分数据展示等问题,那么pandas学习的目的在什么地方呢?
- 便捷的数据处理能力
- 读取文件方便
- 封装了Matplotlib、Numpy的画图和计算
4.1.3 案例:
回忆我们在numpy当中创建的股票涨跌幅数据形式?
# 创建一个符合正太分布的10个股票5天的涨跌幅数据
stock_day_rise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (10, 5))
array([[-0.06544031, -1.30931491, -1.45451514, 0.57973008, 1.48602405],
[-1.73216741, -0.83413717, 0.45861517, -0.80391793, -0.46878575],
[ 0.21805567, 0.19901371, 0.7134683 , 0.5484263 , 0.38623412],
[-0.42207879, -0.33702398, 0.42328531, -1.23079202, 1.32843773],
[-1.72530711, 0.07591832, -1.91708358, -0.16535818, 1.07645091],
[-0.81576845, -0.28675278, 1.20441981, 0.73365951, -0.06214496],
[-0.98820861, -1.01815231, -0.95417342, -0.81538991, 0.50268175],
[-0.10034128, 0.61196204, -0.06850331, 0.74738433, 0.143011 ],
[ 1.00026175, 0.34241958, -2.2529711 , 0.93921064, 1.14080312],
[ 2.52064693, 1.55384756, 1.72252984, 0.61270132, 0.60888092]])
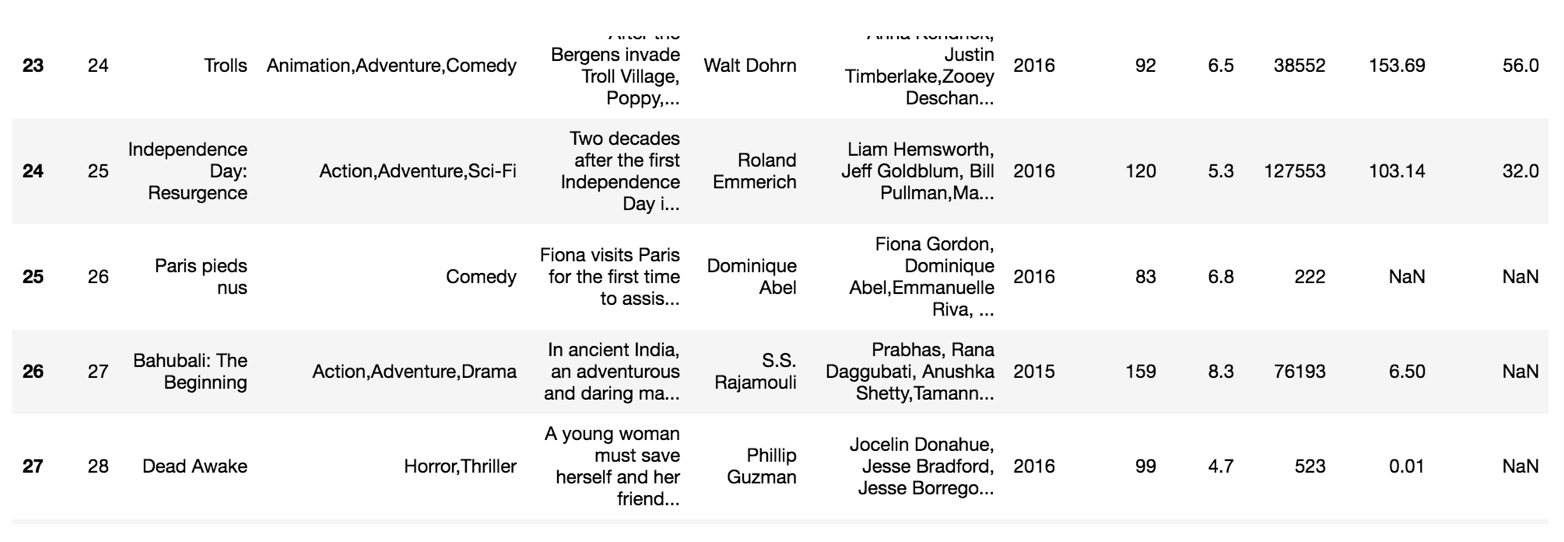
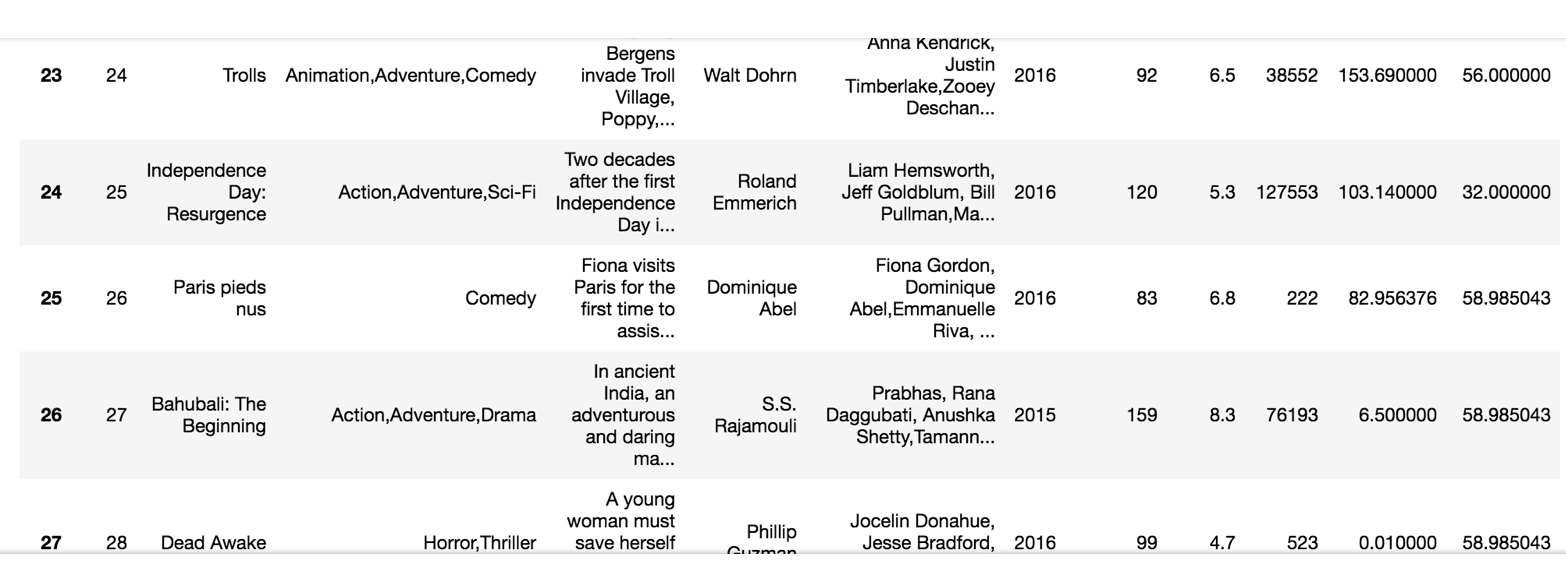
但是这样的数据形式很难看到存储的是什么的样的数据,并也很难获取相应的数据,比如需要获取某个指定股票的数据,就很难去获取!!
问题:如何让数据更有意义的显示?处理刚才的股票数据
# 使用Pandas中的数据结构
stock_day_rise = pd.DataFrame(stock_day_rise)
给股票涨跌幅数据增加行列索引,显示效果更佳
效果:
- 增加行索引
# 构造行索引序列
stock_code = ['股票' + str(i) for i in range(stock_day_rise.shape[0])]
# 添加行索引
data = pd.DataFrame(stock_day_rise, index=stock_code)
- 增加列索引
股票的日期是一个时间的序列,我们要实现从前往后的时间还要考虑每月的总天数等,不方便。使用pd.date_range():用于生成一组连续的时间序列(暂时了解)
date_range(start=None,end=None, periods=None, freq='B')
start:开始时间
end:结束时间
periods:时间天数
freq:递进单位,默认1天,'B'默认略过周末
# 生成一个时间的序列,略过周末非交易日
date = pd.date_range('2017-01-01', periods=stock_day_rise.shape[1], freq='B')
# index代表行索引,columns代表列索引
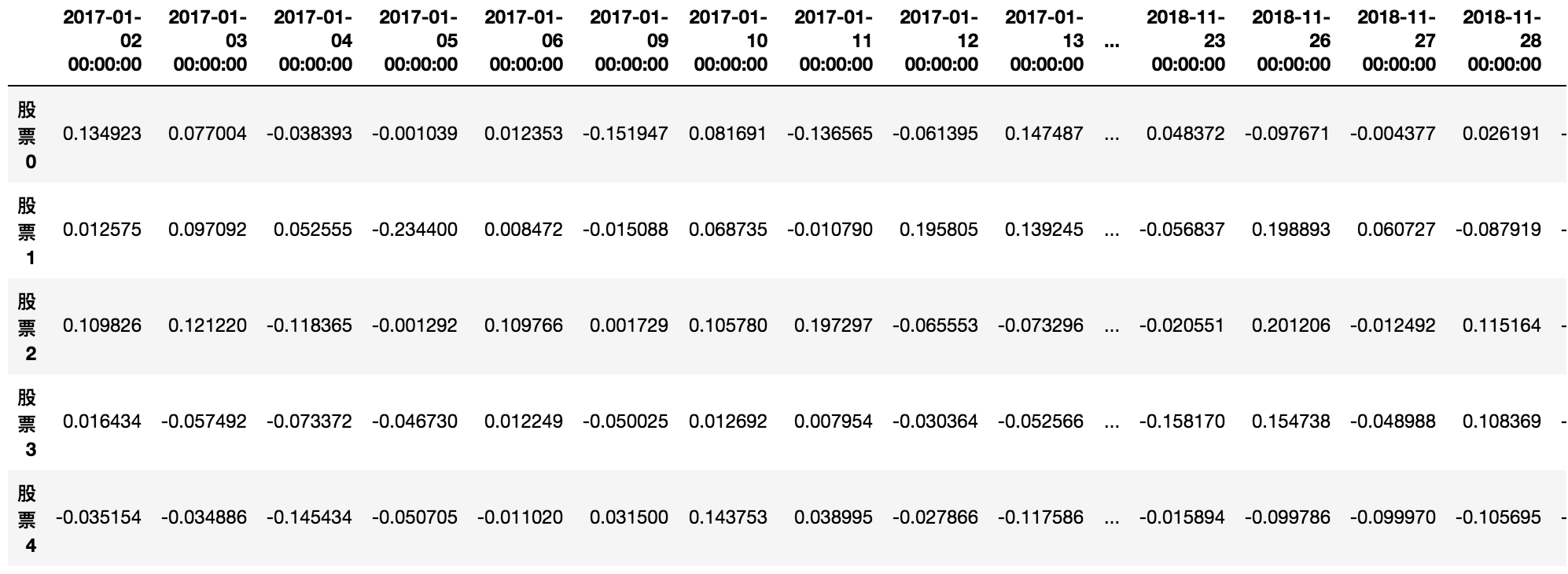
data = pd.DataFrame(stock_day_rise, index=stock_index, columns=date)
4.1.4 DataFrame
4.1.4.1 DataFrame结构
DataFrame对象既有行索引,又有列索引
- 行索引,表明不同行,横向索引,叫index,0轴,axis=0
- 列索引,表名不同列,纵向索引,叫columns,1轴,axis=1
4.1.4.2 DatatFrame的属性
- shape
data.shape
# 结果
(10, 5)
- index
DataFrame的行索引列表
data.index
Index(['股票0', '股票1', '股票2', '股票3', '股票4', '股票5', '股票6', '股票7', '股票8', '股票9'], dtype='object')
- columns
DataFrame的列索引列表
data.columns
DatetimeIndex(['2017-01-02', '2017-01-03', '2017-01-04', '2017-01-05',
'2017-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='B')
- values
直接获取其中array的值
data.values
array([[-0.06544031, -1.30931491, -1.45451514, 0.57973008, 1.48602405],
[-1.73216741, -0.83413717, 0.45861517, -0.80391793, -0.46878575],
[ 0.21805567, 0.19901371, 0.7134683 , 0.5484263 , 0.38623412],
[-0.42207879, -0.33702398, 0.42328531, -1.23079202, 1.32843773],
[-1.72530711, 0.07591832, -1.91708358, -0.16535818, 1.07645091],
[-0.81576845, -0.28675278, 1.20441981, 0.73365951, -0.06214496],
[-0.98820861, -1.01815231, -0.95417342, -0.81538991, 0.50268175],
[-0.10034128, 0.61196204, -0.06850331, 0.74738433, 0.143011 ],
[ 1.00026175, 0.34241958, -2.2529711 , 0.93921064, 1.14080312],
[ 2.52064693, 1.55384756, 1.72252984, 0.61270132, 0.60888092]])
- T
转置
data.T
结果
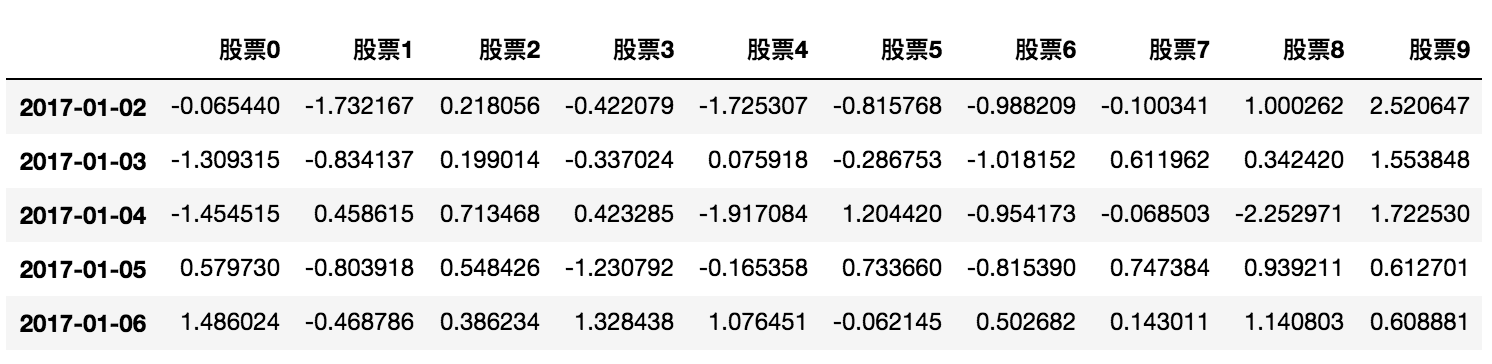
- head(5):显示前5行内容
如果不补充参数,默认5行。填入参数N则显示前N行
data.head(5)
2017-01-02 00:00:00 2017-01-03 00:00:00 2017-01-04 00:00:00 2017-01-05 00:00:00 2017-01-06 00:00:00
股票0 -0.065440 -1.309315 -1.454515 0.579730 1.486024
股票1 -1.732167 -0.834137 0.458615 -0.803918 -0.468786
股票2 0.218056 0.199014 0.713468 0.548426 0.386234
股票3 -0.422079 -0.337024 0.423285 -1.230792 1.328438
股票4 -1.725307 0.075918 -1.917084 -0.165358 1.076451
- tail(5):显示后5行内容
如果不补充参数,默认5行。填入参数N则显示后N行
data.tail(5)
2017-01-02 00:00:00 2017-01-03 00:00:00 2017-01-04 00:00:00 2017-01-05 00:00:00 2017-01-06 00:00:00
股票5 -0.815768 -0.286753 1.204420 0.733660 -0.062145
股票6 -0.988209 -1.018152 -0.954173 -0.815390 0.502682
股票7 -0.100341 0.611962 -0.068503 0.747384 0.143011
股票8 1.000262 0.342420 -2.252971 0.939211 1.140803
股票9 2.520647 1.553848 1.722530 0.612701 0.608881
4.1.4.3 DatatFrame索引的设置
- 修改行列索引值
stock_code = ["股票_" + str(i) for i in range(stock_day_rise.shape[0])]
# 必须整体全部修改
data.index = stock_code
结果
2017-01-02 00:00:00 2017-01-03 00:00:00 2017-01-04 00:00:00 2017-01-05 00:00:00 2017-01-06 00:00:00
股票_0 -0.065440 -1.309315 -1.454515 0.579730 1.486024
股票_1 -1.732167 -0.834137 0.458615 -0.803918 -0.468786
股票_2 0.218056 0.199014 0.713468 0.548426 0.386234
股票_3 -0.422079 -0.337024 0.423285 -1.230792 1.328438
股票_4 -1.725307 0.075918 -1.917084 -0.165358 1.076451
股票_5 -0.815768 -0.286753 1.204420 0.733660 -0.062145
股票_6 -0.988209 -1.018152 -0.954173 -0.815390 0.502682
股票_7 -0.100341 0.611962 -0.068503 0.747384 0.143011
股票_8 1.000262 0.342420 -2.252971 0.939211 1.140803
股票_9 2.520647 1.553848 1.722530 0.612701 0.608881
注意:以下修改方式是错误的
# 错误修改方式
data.index[3] = '股票_3'
- 重设索引
- reset_index(drop=False)
- 设置新的下标索引
- drop:默认为False,不删除原来索引,如果为True,删除原来的索引值
- reset_index(drop=False)
# 重置索引,drop=False
data.reset_index()
index 2017-01-02 00:00:00 2017-01-03 00:00:00 2017-01-04 00:00:00 2017-01-05 00:00:00 2017-01-06 00:00:00
0 股票_0 -0.065440 -1.309315 -1.454515 0.579730 1.486024
1 股票_1 -1.732167 -0.834137 0.458615 -0.803918 -0.468786
2 股票_2 0.218056 0.199014 0.713468 0.548426 0.386234
3 股票_3 -0.422079 -0.337024 0.423285 -1.230792 1.328438
4 股票_4 -1.725307 0.075918 -1.917084 -0.165358 1.076451
5 股票_5 -0.815768 -0.286753 1.204420 0.733660 -0.062145
6 股票_6 -0.988209 -1.018152 -0.954173 -0.815390 0.502682
7 股票_7 -0.100341 0.611962 -0.068503 0.747384 0.143011
8 股票_8 1.000262 0.342420 -2.252971 0.939211 1.140803
9 股票_9 2.520647 1.553848 1.722530 0.612701 0.608881
# 重置索引,drop=True
data.reset_index(drop=True)
2017-01-02 00:00:00 2017-01-03 00:00:00 2017-01-04 00:00:00 2017-01-05 00:00:00 2017-01-06 00:00:00
0 -0.065440 -1.309315 -1.454515 0.579730 1.486024
1 -1.732167 -0.834137 0.458615 -0.803918 -0.468786
2 0.218056 0.199014 0.713468 0.548426 0.386234
3 -0.422079 -0.337024 0.423285 -1.230792 1.328438
4 -1.725307 0.075918 -1.917084 -0.165358 1.076451
5 -0.815768 -0.286753 1.204420 0.733660 -0.062145
6 -0.988209 -1.018152 -0.954173 -0.815390 0.502682
7 -0.100341 0.611962 -0.068503 0.747384 0.143011
8 1.000262 0.342420 -2.252971 0.939211 1.140803
9 2.520647 1.553848 1.722530 0.612701 0.608881
- 以某列值设置为新的索引
- set_index(keys, drop=True)
- keys : 列索引名成或者列索引名称的列表
- drop : boolean, default True.当做新的索引,删除原来的列
- set_index(keys, drop=True)
设置新索引案例
- 1、创建
df = pd.DataFrame({'month': [1, 4, 7, 10],
'year': [2012, 2014, 2013, 2014],
'sale':[55, 40, 84, 31]})
month sale year
0 1 55 2012
1 4 40 2014
2 7 84 2013
3 10 31 2014
- 2、以月份设置新的索引
df.set_index('month')
sale year
month
1 55 2012
4 40 2014
7 84 2013
10 31 2014
- 3、设置多个索引,以年和月份
df.set_index(['year', 'month'])
sale
year month
2012 1 55
2014 4 40
2013 7 84
2014 10 31
注:通过刚才的设置,这样DataFrame就变成了一个具有MultiIndex的DataFrame。
4.1.5 MultiIndex与Panel
打印刚才的df的行索引结果
df.index
MultiIndex(levels=[[1, 2], [1, 4, 7, 10]],
labels=[[0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 2, 3]],
names=['year', 'month'])
4.1.5.1 MultiIndex
多级或分层索引对象。
- index属性
- names:levels的名称
- levels:每个level的元组值
df.index.names
FrozenList(['year', 'month'])
df.index.levels
FrozenList([[1, 2], [1, 4, 7, 10]])
4.1.5.2 Panel
- class
pandas.Panel(data=None, items=None, major_axis=None, minor_axis=None, copy=False, dtype=None)- 存储3维数组的Panel结构
p = pd.Panel(np.arange(24).reshape(4,3,2),
items=list('ABCD'),
major_axis=pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3),
minor_axis=['first', 'second'])
p
<class 'pandas.core.panel.Panel'>
Dimensions: 4 (items) x 3 (major_axis) x 2 (minor_axis)
Items axis: A to D
Major_axis axis: 2013-01-01 00:00:00 to 2013-01-03 00:00:00
Minor_axis axis: first to second
- items -
axis 0,每个项目对应于内部包含的数据帧(DataFrame)。 - major_axis -
axis 1,它是每个数据帧(DataFrame)的索引(行)。 - minor_axis -
axis 2,它是每个数据帧(DataFrame)的列。
注:Pandas从版本0.20.0开始弃用:推荐的用于表示3D数据的方法是通过DataFrame上的MultiIndex方法
如果获取DataFrame中某个股票的不同时间数据?这样的结构是什么样的?
4.1.6 Series结构
什么是Series结构呢,我们直接看下面的图:
- series结构只有行索引
我们将之前的涨跌幅数据进行转置,然后获取'股票0'的所有数据
# series
type(data['股票0'])
pandas.core.series.Series
# 这一步相当于是series去获取行索引的值
data['股票0']['2017-01-02']
-0.18753158283513574
4.1.6.1 创建series
通过已有数据创建
- 指定内容,默认索引
pd.Series(np.arange(10))
- 指定索引
pd.Series([6.7,5.6,3,10,2], index=[1,2,3,4,5])
通过字典数据创建
pd.Series({'red':100, ''blue':200, 'green': 500, 'yellow':1000})
4.1.6.2 series获取属性和值
- index
- values
4.1.7、小结
- 说明pandas的三种数据结构